
For the F statistic there are two separate degrees of freedom - one for the numerator and one for the denominator.įinally, to determine a critical region, one needs to know whether they are testing a point null versus a composite alternative (on both sides) or a composite null versus (covering one side of the distribution) a composite alternative (covering the other). Then, for distributions other than the normal one (Z), you need to know the degrees of freedom.

F-distributed (Fisher-Snedecor distribution), usually used in analysis of variance (ANOVA).X 2-distributed ( Chi square distribution, often used in goodness-of-fit tests, but also for tests of homogeneity or independence).T-distributed (Student's T distribution, usually appropriate for small sample sizes, equivalent to the normal for sample sizes over 30).Z-distributed (normally distributed, e.g.Our critical value calculator supports statistics which are either: Then you need to know the shape of the error distribution of the statistic of interest (not to be mistaken with the distribution of the underlying data!). For example, 95% significance results in a probability of 100%-95% = 5% = 0.05. If you know the significance level in percentages, simply subtract it from 100%. You need to know the desired error probability ( p-value threshold, common values are 0.05, 0.01, 0.001) corresponding to the significance level of the test. significance test, statistical significance test), determining the value of the test statistic corresponding to the desired significance level is necessary. The probability of a Type II Error can be calculated by clicking on the link at the bottom of the page.If you want to perform a statistical test of significance (a.k.a. These can be solved using the Two Population Calculator. Sometimes we're interest in hypothesis tests about two population means. The calculator on this page does hypothesis tests for one population mean. Confidence intervals can be found using the Confidence Interval Calculator. If the hypothesized value of the population mean is outside of the confidence interval, we can reject the null hypothesis. Hypothesis testing is closely related to the statistical area of confidence intervals. Ideally, we'd like to reject the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true. A Type II Error is committed if you accept the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true. Ideally, we'd like to accept the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true. A Type I Error is committed if you reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true. There are two types of errors you can make: Type I Error and Type II Error.
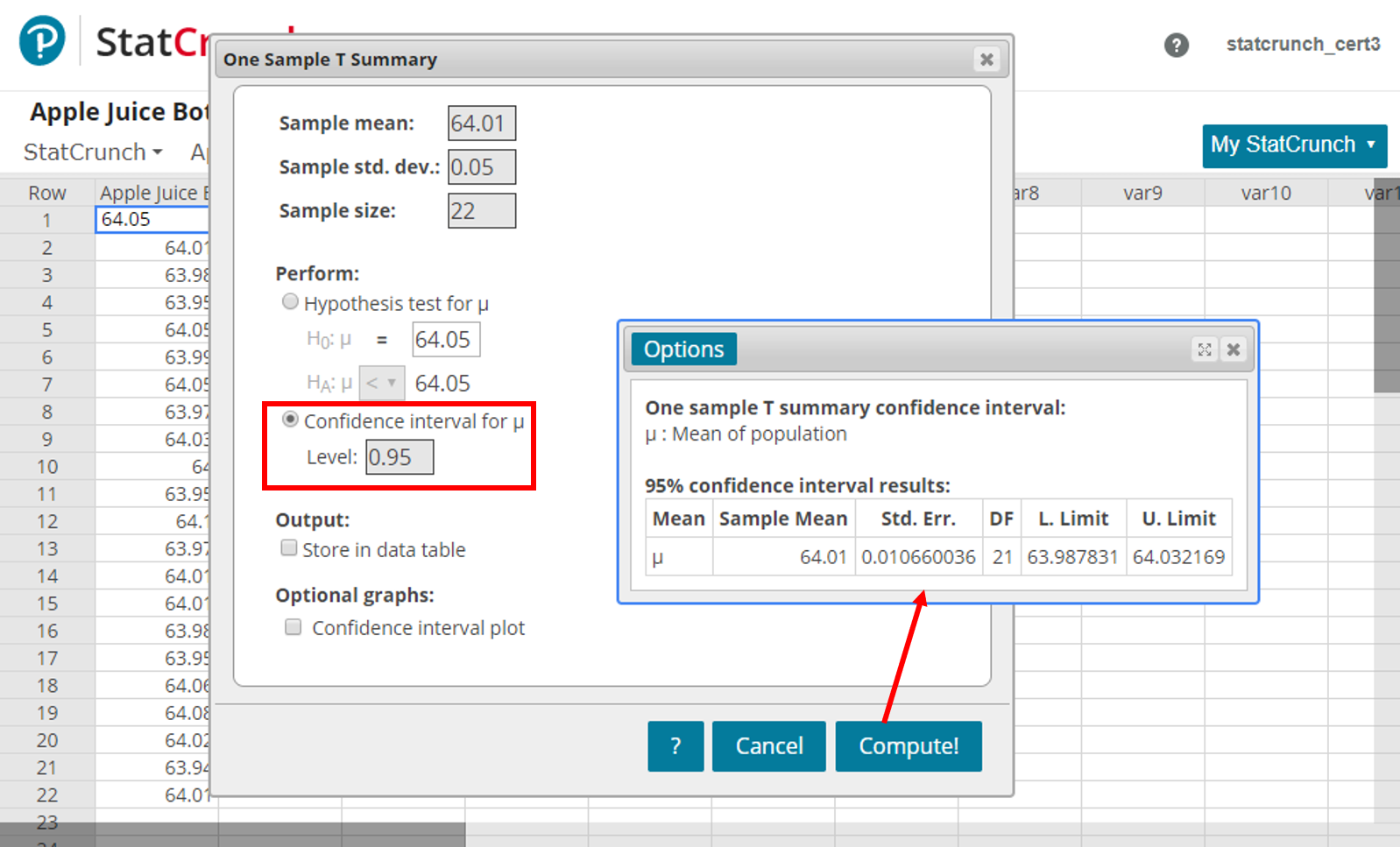
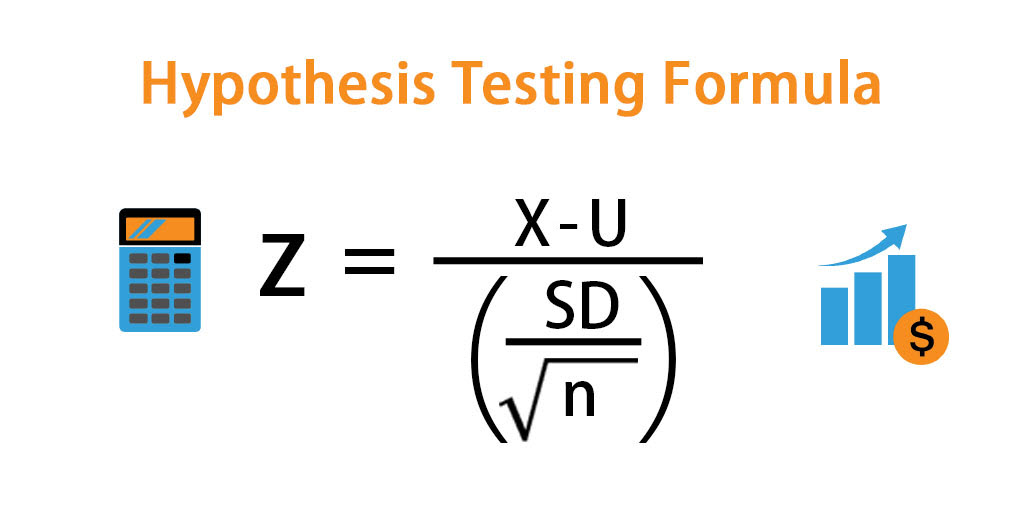
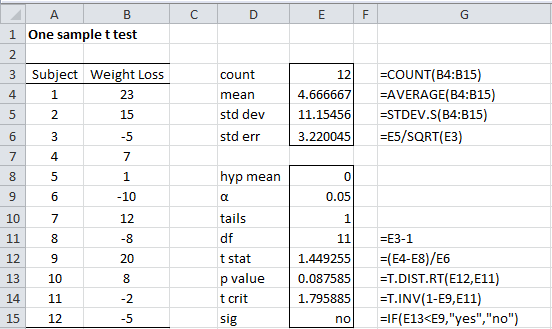
When conducting a hypothesis test, there is always a chance that you come to the wrong conclusion. To switch from σ known to σ unknown, click on $\boxed$, reject $H_0$. Furthermore, if the population standard deviation σ is unknown, the sample standard deviation s is used instead. Use of the t distribution relies on the degrees of freedom, which is equal to the sample size minus one. If σ is unknown, our hypothesis test is known as a t test and we use the t distribution. If σ is known, our hypothesis test is known as a z test and we use the z distribution. The formula for the test statistic depends on whether the population standard deviation (σ) is known or unknown. The first step in hypothesis testing is to calculate the test statistic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
